“Blockchain” refers to a shared irreversible record of a chain of transactions, each of which is made up of one block, and which is held together by cryptographic keys (“hashes”). These keys or signatures are maintained in shared ledgers and connected by a network of nodes or processes. Each node maintains a copy of the entire chain, which is constantly synchronised and updated.
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the advantages of blockchain technology include its tamper-resistant nature, the decentralised nature of digital ledgers, and the inability to change a published transaction later within the user community that shares the ledger. The term “digital ledger technology” (DLT) refers to this technology.
What does the blockchain excel at?
- Tracking / registry: Keeping track of information and data in a permanent and transparent manner, with no unequal authority over the data.
- Data access / transfer: Facilitating data flow between various parties in order to establish a single source of “truth”
- Identity/authentication: Ability to validate identity attributes without revealing sensitive data along with handling identities and consents for authentication or verification.
- Settlements: Recording the movement of goods/revenues or the use of services/assets in order to settle revenue.
- Transactions: Making payments and transactions possible in real time.
- Token exchange: Multiple parties trade virtual currency/tokens with intrinsic value. Virtual currencies can also be tied to fiat currencies, with escrow accounts holding equal values.
Blockchain In Healthcare:

Blockchain technology has grown in popularity in recent years, attracting interest from a variety of industries including finance, government, energy, and health. This article discusses the use of blockchain in the healthcare industry. In fact, continuing research in this field is quickly progressing. As a result, we’ve identified various state-of-the-art use cases for blockchains, such as sharing electronic medical data, remote patient monitoring, medicine supply chain, and so on.
Given the enormous challenges that healthcare systems face in terms of digitising and sharing medical records, as well as tracking prescription drugs and other medical goods throughout the supply chain and delivery, it’s no surprise that many are attempting to improve processes in healthcare using blockchain technology.
Blockchain technology has proven to be a reliable solution for a variety of issues in the healthcare industry, including data breaches and counterfeit drugs.
Applications of Blockchain in Healthcare:
Below are a few ways blockchain is helpful in the healthcare industry.
1. Security and Patient Data Management

In the healthcare industry, data security is a critical concern. Data security has become a major issue for patients around the world as the number of data breaches rises year after year. Fortunately, today’s blockchain healthcare applications include maintaining data security.
Blockchain technology is a distributed, unchangeable ledger of records that is decentralised and distributed. Because of the technology’s high security features, any information saved on the blockchain becomes nearly hard to hack or change. Because it provides openness, any changes in information are obvious, and the data cannot be changed. As a result, blockchain technology enables providers and patients to transmit critical healthcare information speedily and securely, while also ensuring privacy and transparency through encryptions and complicated security codes. Below are a few ways it happens;
● With the use of smart contracts, healthcare institutions or providers can save patient health records on the blockchain.To access the data, a public key, also known as a unique ID, is established.
● A doctor must have the patient’s public key in order to access the information. Only when the key or unique ID matches does the data become visible to the healthcare provider.
Without the public key, no blockchain healthcare system can reveal the information contained on it. As a consequence, patients can share their public key as needed with healthcare professionals.This key will give institutions access to data while protecting the patient’s identity because the data will be unidentifiable without it.
2. Genomics

Genomic data theft has become a big issue as more companies deliver DNA sequencing to the individual. This can be avoided using blockchain, and it can even be used to create an online marketplace where scientists can acquire genomic data for research reasons. This could encourage secure selling while obviating the need for costly middlemen.
Blockchain services could be used to improve the administration of healthcare data with increased blockchain security and systems that promote synchronized transactions.
3. Improving Communication between Care providers and Patients
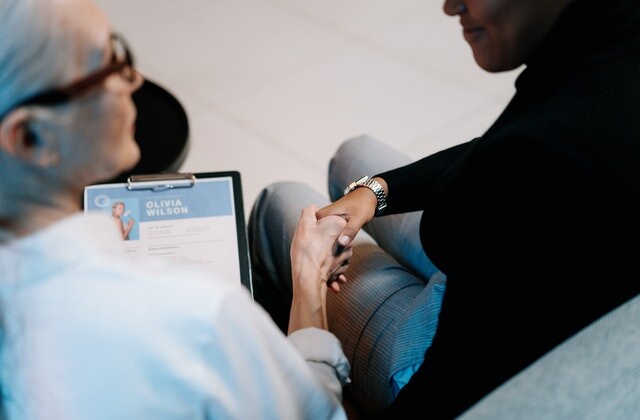
Miscommunication is a flaw that has a negative impact on every industry, regardless of its values. Because people’s lives are on the line, it’s important to maintain seamless and effective communication, especially in a sensitive sector like healthcare. Miscommunication between healthcare practitioners or between patients and providers may be expensive and even harmful to the health of patients. The majority of miscommunications are caused by erroneous medical records or delays in updating due to the lengthy process.
Blockchain technology might be a potential answer to this problem. There are decentralised blockchain solutions on the market. As a result, rather than being kept in a single database, the information is dispersed among several network nodes. When information in one node is altered or updated, all network nodes are updated as well. It streamlines the process of exchanging up-to-date information with any doctor or healthcare provider. The information kept on a blockchain is legitimate, up-to-date, and timestamped, making it simple for providers to review and act on it, especially in the event of an emergency. It also aids clinicians in creating more individualised treatment programmes and completing diagnoses more quickly.
4. Control of Pharmaceutical Counterfeiting

Counterfeiting of pharmaceuticals is a major issue in the healthcare sector. There is a lot of tampering and counterfeiting in pharmaceutical supply chains since they aren’t transparent. Because it gives system transparency and immutability, blockchain technology is a great way to combat pharmaceutical counterfeiting. It gives the supply chain total end-to-end visibility. In the pharmaceutical supply chain, blockchain can help suppliers manage inventory, reduce counterfeiting problems, and reduce theft.
It can also assist organizations such as the Red Cross, USAID, and the Global Fund in tracing the flow of donated medications throughout countries while assuring the pharmaceuticals’ provenance, validity, and integrity.
5. Research

Electronic health records currently only allow for the automatic updating and sharing of medical information on a single patient inside a single organization or network of organizations. This might be extended if the data was arranged so that the uppermost layer of the blockchain only contained information that was not PHI or personally identifiable information (PII).
This might be extended if the data was arranged so that the uppermost layer of the blockchain only contained information that was not PHI or personally identifiable information (PII). Researchers and other organizations would be able to access a broad range of data, including patient cohorts numbering in the hundreds of thousands. Clinical research, safety event and adverse event reporting and identification, and public health reporting would all benefit significantly from having such vast amounts of data available.
6. Smoother transition of patients among Care providers

Individual patients might use the same information on the blockchain to quickly unlock and share their health data with other physicians or organizations using a shareable private key. This could aid in the interoperability and collaboration of health information technology (HIT) among diverse users.
7. Quick, Economical and Quality Patient Care

Blockchain has the potential to build a single system for storing and retrieving health records in a secure and timely manner by authorised users. Innumerable mistakes can be avoided, faster diagnoses and interventions are possible, and care can be individualised to each patient by eliminating miscommunication between different healthcare personnel involved in caring for the same patient.
8. Compatible electronic health records

By keeping a specified set of standardized data on the chain, together with private encrypted links to separately stored information such as radiographic or other images, the blockchain might enable a single transaction layer where businesses can submit and share data through one secure mechanism.
The usage of smart contracts and standardized authorization standards can greatly aid in the provision of seamless connectivity.
9. Data Security

The blockchain’s secure characteristics can significantly improve the security of health data. Each person has a public identification or key and a private key that can only be opened when and for the duration of time required.
Furthermore, the requirement to attack each user individually in order to obtain sensitive information would limit hacking. As a result, blockchains can provide an immutable audit trail of medical data.
10. Remote monitoring and mobile health applications

With the advancement of technology, mobile health applications are becoming increasingly vital. Electronic medical records (EMRs) were discovered to be kept secure on a blockchain network, and the data could be transferred to medical workers quickly, as well as used for self-monitoring and home care. This area is particularly vulnerable to malware, particularly root exploits that allow a hacker to obtain the patient’s private key.
11. Review of medical staff records

Blockchain technology can be used to track the experience of medical professionals in the same way that it can be used to track the provenance of a medical good. Trusted medical institutions and healthcare organisations can log the credentials of their staff, which helps to streamline the hiring process for healthcare organisations. The following are the main advantages of the blockchain system:
- During the employment process, healthcare organisations will be able to get credentialed more quickly.
- A chance for medical institutions, insurers, and healthcare providers to profit from their existing credentials data on previous and current employees.
- Transparency and assurance for partners, such as organisations that subcontract locum tenens or in new virtual health care models to educate patients about medical staff experience
12. IoT security for remote monitoring

One of the key breakthroughs in digital health is the use of remote monitoring systems, in which all sorts of sensors detecting patients’ vital signs are used to assist healthcare practitioners with improved insight into patients’ health, enabling more proactive and preventative care. However, security is a major concern in health IoT, both in terms of keeping patient data private and safe and preventing it from being tampered with to generate misleading data.In some circumstances, when a connected device may be relied on in an emergency situation, such as informing an elderly person’s caregiver that they have fallen or had a heart attack, it is equally critical that the supporting systems are highly robust to DDoS or other assaults interrupting service.
Here’s how blockchain technologies might aid in the safe monitoring of IoT devices in the field:
Personal data is saved on the blockchain as a unique hash function, and blockchain cryptography guarantees that only authorised parties have access to it (any change in the source data will create a different hash function, and a user must have a specific set of cryptographic keys to decode the hash function into the source data).It’s almost difficult to tamper with patient data after it’s recorded on the blockchain ledger (as a hash function), because doing so would necessitate getting access to all stored copies.
Because of the decentralised nature of blockchain, IoT devices may interact directly with each other instead of going through a centralised server (like most IoT connections do today), making DDoS and man in the middle attacks extremely difficult.
13. Tracking and securing medical supplies
With complete transparency, blockchain can assist safeguard and identify the trail of pharmaceutical supply. It can even track the labor expenses and carbon emissions associated with the production of these items.
14. Health Insurance claims

Because of its capacity to display medical events as they occurred without the possibility of altering the data later for fraud reasons, the blockchain is particularly suited to claim processing.
15. Monitor diseases and disease outbreaks
The unique features of blockchain can aid real-time disease reporting and disease pattern analysis, which can aid in determining the disease’s origin and transmission factors.
Conclusion
In the healthcare business, blockchain technology has a variety of applications, and with its rising popularity, we may see even more in the future. To address the substantial issues that this sector confronts, it is critical to make changes and enhance the quality of healthcare services provided. The use of blockchain technology looks to be a viable option. Blockchain technology, with appropriate implementation and solid applications, has the potential to be the saviour the healthcare sector has been yearning for.
ERP vs CRM: Key Differences, Strengths, and How Clavis’ ERP Drives Organizational Success
In the digital age, businesses strive to leverage advanced tools to streamline operations, boost productivity, and foster better customer relationships. Two pivotal software solutions that play a significant role in achieving these goals are Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. While these tools may seem similar at first glance, they serve distinct purposes and offer unique benefits, and it is important to understand why you may need one or the other—or both in tandem.
1. What is ERP?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, a comprehensive software suite that manages and integrates core business processes. These processes often include:
- Finance and accounting
- Human resources
- Supply chain management
- Inventory and order management
- Manufacturing
ERP systems centralise business data, allowing various departments to collaborate seamlessly and make informed decisions based on real-time insights.
Core Features of ERP Systems
- Centralized Data Management: Consolidates information from all business departments into one platform.
- Process Automation: Automates repetitive tasks to improve efficiency.
- Scalability: Can grow with your business, accommodating new functionalities as needed.
- Compliance Support: Helps organisations meet regulatory requirements.
- Advanced Analytics: Provides detailed insights to support strategic decision-making.
2. What is CRM?
CRM, or Customer Relationship Management, is software that focuses on managing a company's interactions with current and potential customers. The primary goal of a CRM system is to improve customer satisfaction, retention, and acquisition through personalised communication and efficient management of sales and marketing activities.
Core Features of CRM Systems
- Contact Management: Maintains detailed records of customer interactions and preferences.
- Sales Pipeline Tracking: Manages leads and monitors the sales process.
- Marketing Automation: Facilitates email campaigns, social media management, and more.
- Customer Support: Enhances post-sale services through ticketing systems and live chats.
- Data-Driven Insights: Helps identify trends to fine-tune marketing and sales strategies.
3. ERP vs. CRM: Key Differences
While ERP and CRM are essential for business success, they cater to different aspects of operations.
|
Feature |
ERP |
CRM |
|
Primary Focus |
Internal processes and operational efficiency |
Customer interactions and relationships |
|
Key Functions |
Accounting, supply chain, HR, inventory |
Sales, marketing, customer service |
|
Target Audience |
Internal stakeholders |
Sales, marketing, and customer support teams |
|
Data Integration |
Focuses on consolidating operational data |
Specialises in customer-centric data |
|
Scalability |
Enterprise-wide |
Primarily focused on customer management |
4. The Strengths of ERP Systems
ERP systems are the backbone of operational efficiency. Their key strengths include:
- Holistic Business View: ERP provides a comprehensive view of business operations by integrating data across departments.
- Cost Reduction: Automating processes reduces manual labour and errors, saving time and money.
- Improved Compliance: Centralized data simplifies regulatory reporting and ensures adherence to standards.
- Inventory Optimization: Enhances inventory management, reducing waste and ensuring timely procurement.
- Agile Decision-Making: Real-time data insights help leaders make swift, informed decisions.
5. The Strengths of CRM Systems
CRM systems shine in the realm of customer relationship management, with benefits such as:
- Enhanced Customer Insights: Tracks and analyses customer preferences to tailor interactions.
- Improved Customer Retention: Personalization and timely communication foster loyalty.
- Streamlined Sales Processes: Automates lead management, reducing manual intervention.
- Marketing Optimization: Helps segment audiences for targeted campaigns.
- Boosted Collaboration: Facilitates alignment between sales and marketing teams.
6. ERP and CRM: Complementary Tools
Though distinct, ERP and CRM systems are complementary and often integrated to deliver maximum value. For instance:
- CRM manages the front-end relationship with customers, while ERP handles back-end processes like inventory and order fulfilment.
- Together, they provide a seamless flow of information, ensuring that customer-facing teams have accurate, up-to-date data on orders and services.
7. Clavis' ERP: The Ultimate Solution for Organizational Success
Clavis' ERP stands out as a robust ERP solution designed to address the multifaceted needs of modern businesses. Here’s how it can drive your organisation's success:
a) Comprehensive Integration
Clavis' ERP integrates seamlessly with existing systems, including CRM platforms, to unify your business processes.
b) Real-Time Data Analytics
With Clavis' ERP, decision-makers can access advanced analytics tools that offer actionable insights into performance, trends, and potential opportunities.
c) Tailored Functionality
Highly customisable to suit the unique needs of businesses across industries, Clavis' ERP works for all—from manufacturing to retail and more.
d) Enhanced User Experience
The platform boasts an intuitive interface, making it easy for employees to adopt and use effectively.
e) Cloud Capabilities
Leverage cloud-based deployment for flexibility, scalability, and cost savings.
9. Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
When deciding between ERP and CRM—or opting for an integrated approach—consider the following:
- Business Goals: Identify whether your primary focus is operational efficiency (ERP) or customer relationships (CRM).
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can grow with your business.
- Budget: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including deployment and maintenance.
- Customization: Ensure the platform can be tailored to your specific needs.
Final Thoughts
ERP and CRM systems are indispensable for businesses aiming to optimise operations and enhance customer relationships. While they serve distinct purposes, their integration offers unparalleled value. With Clavis' ERP, you gain a robust tool that streamlines your operations and integrates seamlessly with CRM systems to provide a holistic business solution.
Some other posts you might be interested in.

AI + RPA: The Ultimate Duo to Scale Your Business Faster and Smarter
Scaling a business isn’t just about doing more—it’s about doing more intelligently. As digital transformation redefines the modern enterprise, two technologies have emerged as transformative powerhouses: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotic Process Automation...
Effortless and Effective Digital Signage for Every Organization with Clavisign
Explore how digital signage from Clavisign is transforming business communication and engagement.

Benefits of Blockchain for Supply Chain Management Solutions
With the increasing number of stakeholders and the different roles played by them, supply chain management has become a complicated and cumbersome process. Simple transactions have turned into lengthy procedures as the clients, suppliers, and providers get to interact...
